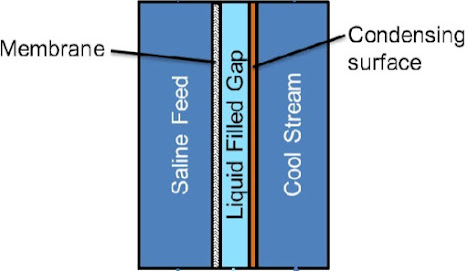
Membrane Distillation is a promising technology for treating saline water and wastewater with high rejection factors, which cannot be accomplished by conventional technologies.
Membrane Distillation uses low-grade thermal energy to drive desalination, to remove non-volatile contaminants or to recover other components. In the Membrane Distillation process, only vapor molecules are allowed to pass through the hydrophobic membrane pores. The pressure difference resulting from the temperature difference is applied between the surfaces of the hydrophobic membrane, so the separation takes place.
Compared with other conventional separation technologies such as reverse osmosis, nanofiltration, or thermal distillation, Membrane Distillation is very attractive due to mild operating conditions such as low temperature and atmospheric pressure, and 100% theoretical salt rejection.
Other key advantages of membrane distillation processes over conventional separation technologies are:
*Relatively lower energy costs as compared to distillation, reverse osmosis, and pervaporation;
*A considerable rejection of dissolved, non-volatile species;
*Much lower membrane fouling as compared with microfiltration, ultrafiltration, and reverse osmosis; reduced vapor space as compared to conventional distillation
Membrane Distillation has gained wide attention in the last decade for various separation applications, including the separation of salts, toxic heavy metals, oil, and organic compounds from aqueous solutions.
The most used membranes for Membrane Distillation are polypropylene (PP), polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). Among these, PTFE has advantages such as high chemical stability, high crystallinity, low intermolecular attraction, low surface energy, and high hydrophobicity.
Membrane Distillation
Food science is the study of food's composition, properties, and interactions with biological and chemical processes. It explores how food is processed, preserved, and safely consumed. By combining biology, chemistry, and nutrition, food science improves food quality, enhances flavor, and ensures safety for global consumption.
The Most Popular Post
-
Anethole is primarily extracted from plants like anise, fennel, and star anise through various methods, with steam distillation and solvent...
-
Drinking decaf tea offers numerous health benefits, making it an excellent choice for those who want to enjoy tea without the stimulating e...
-
Phosphorus is a vital mineral for the human body, playing a crucial role in the development and maintenance of bones and teeth. It is also i...
-
Selenium, a trace element discovered by Swedish chemist Berzelius in 1817, emerges as a potent yet often overlooked weapon in the fight agai...
-
Beginning in the 1990s, scientists embarked on a revolutionary journey by creating numerous genetically modified (GM) food varieties. This m...